Introduction
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), known as a drone in common parlance, is an airborne system that is operated remotely by a human or guided autonomously by an onboard computer. They have earned the recognition of being third-generation platforms for yielding remotely sensed data of the Earth’s surface.
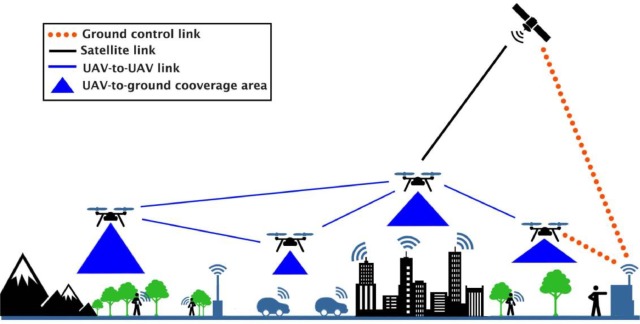
What is Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing is an advanced methodology of surveying and data analysis that employs airborne sensors to generate crucial environmental, geo-spatial and structural information. It converts raw images into three-dimensional maps to provide deeper insights of temporal and spatial features of the environment.
How does Remote Sensing work?
Every matter reflects, transfers and absorbs energy. Objects can be determined by studying their interaction with energy sources via high-powered sensors. The most common metric in remote sensing is the light on the visible spectrum. Infrared lights and ultraviolet radiation are important for specialty purposes. Advanced sensors collect wavelength data from the target objects in the form of infrared readings and images.
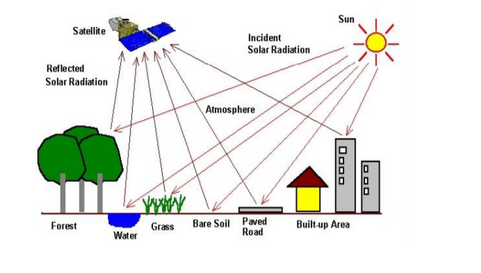
Applications of Remote Sensing
Today remote sensing is increasingly being used to generate insightful, real-time information. The areas where remote sensing is employed are:
-
Agriculture: Remote sensing helps in assessing biomass of various crops and in studying phenomena like vegetation growth, droughts, erosion, stress etc. It also helps to keep a track of the changes in the landform
over a period of time so that necessary agricultural practices/remedies can be undertaken.
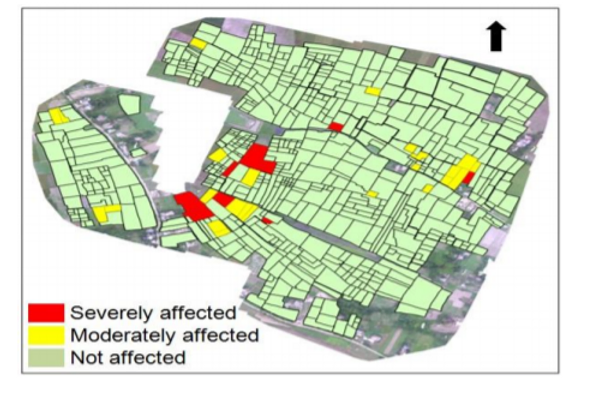
Example: The Infested Crop Damage Assessment carried out in Naramari village, Morigaon District, Assam wherein Boro Paddy was severely infested by Brown Plant Hopper (BPH) insect - Oil and Gas: Remote sensing plays a great role in surveying areas for the construction and inspection of pipelines. It gives a fillip to the oil and gas industry by identifying potential natural resources.
- Telecom: The imagery obtained from remote sensing makes the risky job of inspecting power lines and cell towers relatively easier. The maintenance tasks of the telecom sector can be performed more efficiently using remote sensing.
- Forest Management: Remote sensing contributes a great deal in forest and landscape management and planning. It also helps in determining and monitoring the forest cover of remote areas.
- Water Quality Monitoring: Remote sensing collects water quality data for innumerable lakes at a time. It helps in addressing and studying issues like water colour, turbidity, clarity etc.

The future of Remote Sensing Remote sensing has become an integral part of engineering and research as it empowers researchers with valuable insights of the natural cycle. With time, drones will get cheaper and more accessible. However, proper training, approved drone resignation and new innovations must be focused upon for a risk-free conducive environment for remote sensing.

